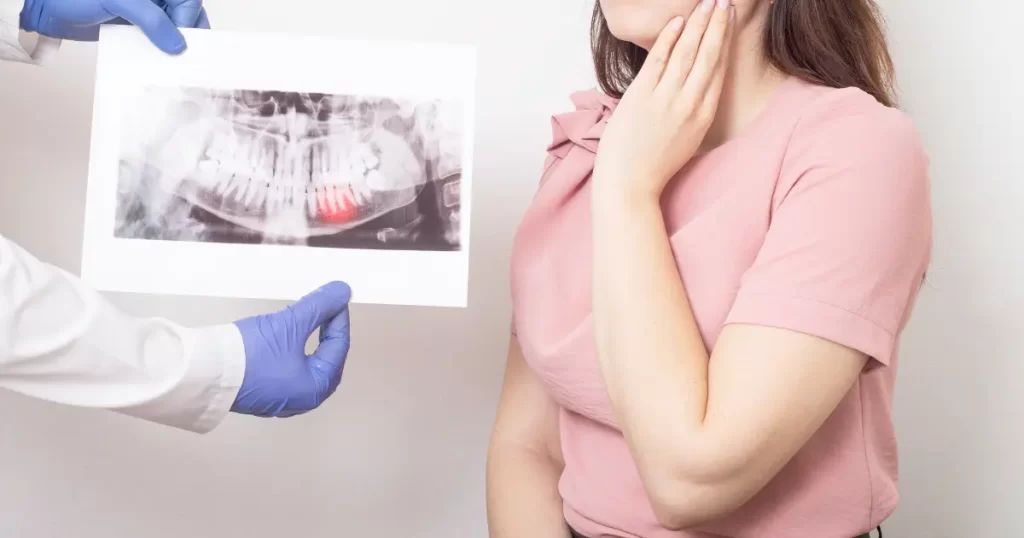
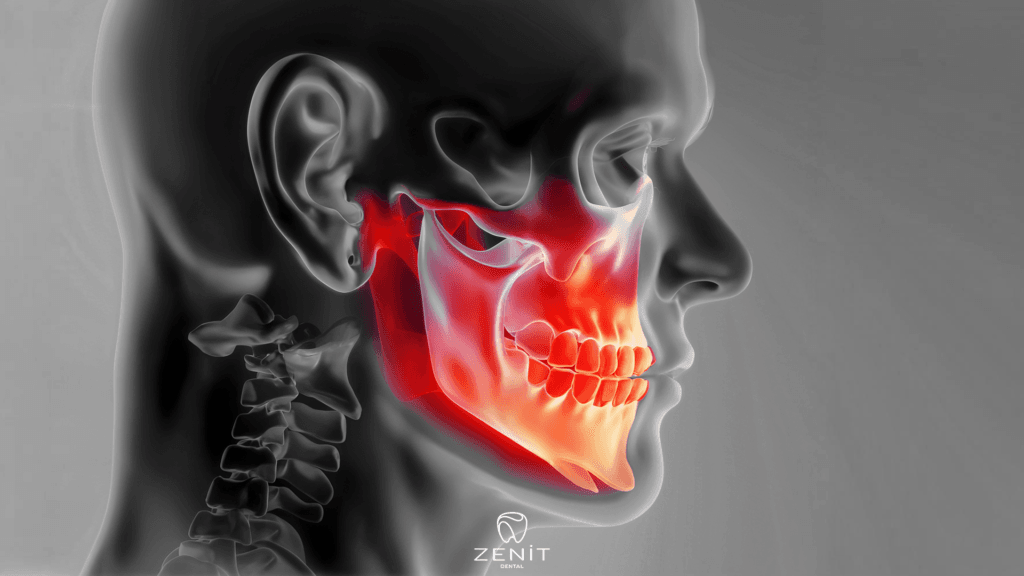
Are you enduring acute dental pain? You may have noticed that the color of your teeth has changed or that your gums or jaw are swollen. Do you have difficulty opening your mouth, a horrible taste on your tongue, or terrible breath? A severe tooth infection may be the cause.
You have several nerves in your teeth. Even though a toothache may just affect one part of your mouth, the agony can be excruciating. Additionally, the discomfort could occasionally be a symptom of a more serious oral health problem. If you suspect a tooth infection or abscess, don’t forget to call your dentist right away.
What Are Common Symptoms of a Tooth Infection?

There are a few primary signs of a tooth infection:
- Excessive sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods
- Change in tooth color
- Enlargement of the face, jaw, mouth, or lymph nodes adjacent
- Elevated swelling resembling a pimple around the teeth
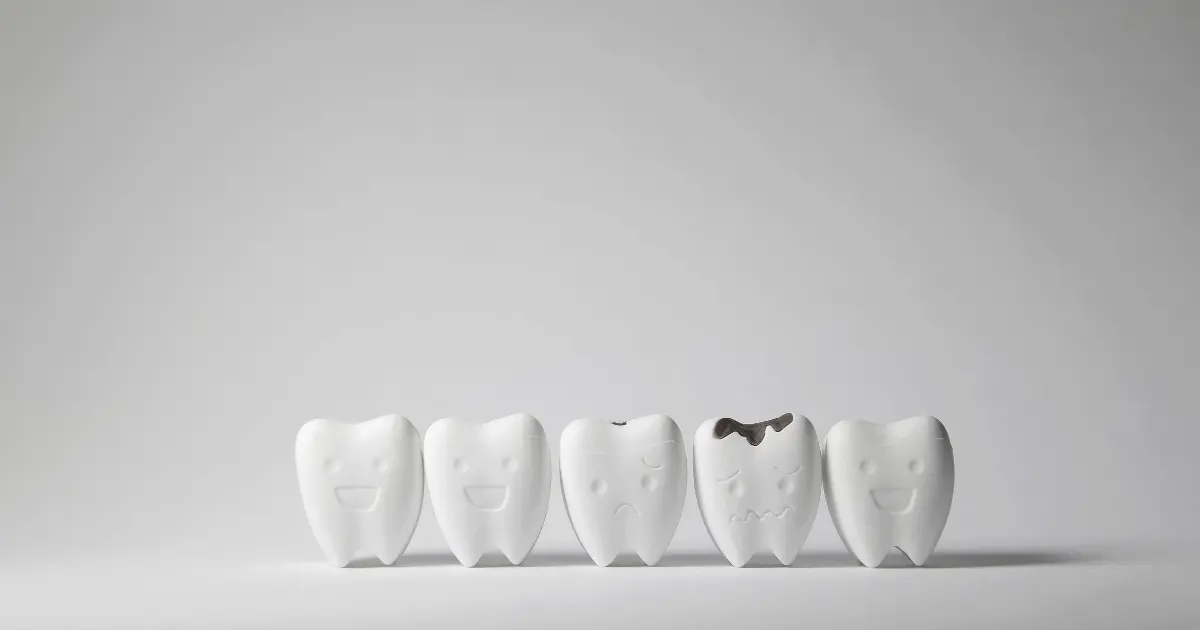
A tooth abscess is a pus-filled pocket resulting from a bacterial infection. Abscesses can form in numerous areas around a tooth due to a variety of factors, affecting not just the affected tooth but also the surrounding bone and, on occasion, the adjacent teeth. This condition originates in the gums. It typically has little effect on the tooth or its supporting structures.
A periapical abscess refers to an infection that originates around the root tip. This occurs because bacteria can enter the pulp of the tooth through a crack or cavity. The pulp, located within the tooth, contains blood arteries and nerves. When bacteria invade the pulp, they may go to the tooth’s root tip, where they may convey the infection to the bone, resulting in an abscess.
This infection initially manifests in the supporting tissues and bone of the tooth. Periodontal abscesses, which are commonly caused by periodontitis or gum disease, are more prevalent in adults than in children.
How Is a Tooth Infection Treated?

Your specific needs will be considered while creating your tooth abscess treatment. The most effective method for treating an abscessed or infected tooth is drainage. Using a small incision, pus can be drained from the abscess. Additionally, the dentist may do debridement, saline irrigation, or cleaning of the affected area. Debridement is the removal of necrotic or nonregenerative tissue.
Abscess drainage is not always straightforward or even possible. A severe oral infection might “neutralize” the effects of local anesthetics, making it more difficult to numb the patient for treatment. When an infection of the lower molars is serious, it is more difficult to numb those teeth. In such cases, it is vital to put the patient on the appropriate antibiotic to reduce the infection before administering local anesthetics.
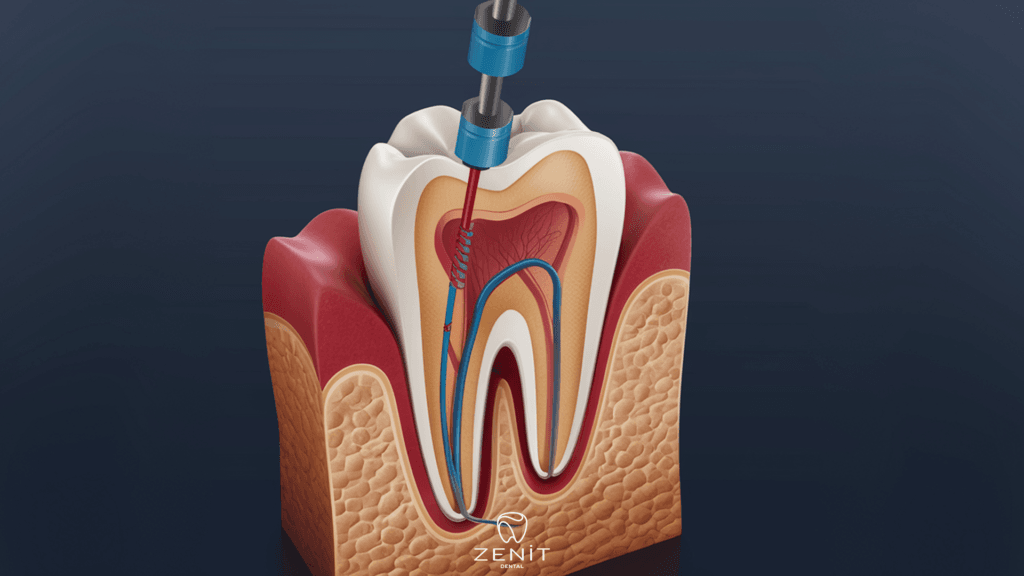
During a root canal, the nerve, artery, and vein situated at the center of the tooth root are removed. A root canal can aid in emptying an abscess and eliminating infection from an affected tooth. When the infection has subsided, a crown is placed over the tooth to restore its strength and ensure its continued health.
Can A Tooth Infection Spread to Other Parts of The Body?

Yes, a tooth infection can have an impact on the entire body. A tooth infection can get so serious that it affects your face, sinuses, neck, jawbone, blood, and possibly your entire body. Your tooth might become infected if you ignore your painful and aching tooth. Without treatment, an infection in your tooth might spread to other parts of your body.
A tooth abscess can have a significant negative effect on your general health in addition to foul breath and susceptibility to high temperatures. Untreated tooth infections can become systemic and result in conditions including sepsis, lung actinomycosis, and brain abscesses.
Consult a physician or dentist if you have unexpected changes in taste and smell. As a caregiver, assist elderly persons in brushing and flossing their teeth if they are unable to do so themselves.
How Can I Prevent a Tooth Infection?
Consuming fluoridated water is recommended. Use fluoride toothpaste and brush your teeth at least twice daily for two minutes. Daily flossing with dental floss or a water flosser is recommended. Every three to four months, or when the bristles start to break down, you should get a new toothbrush.
Consume nutritious foods and avoid between-meal snacks and sugary beverages. See your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. Consider using an antiseptic or fluoride mouthwash to give an additional layer of defense against tooth decay.
Every six months, see the dentist. A dentist has access to parts of your mouth and teeth that you cannot see in a mirror. They have the training and a third-person perspective to recognize problems before you do. Early detection is the first rule of prevention. The sooner it can be treated, the less likely it is to become a serious health problem.